Cardiac Exercise Stress Test - "Stress Test"
A cardiac exercise stress test is a test that shows how well your heart handles exercise.
What is a cardiac exercise stress test?
Why do I need a cardiac exercise stress test?
What are the risks of having a cardiac exercise stress test?
How do I prepare for a cardiac exercise stress test?
What happens during a cardiac exercise stress test?
What happens after a cardiac exercise stress test?
What is a cardiac exercise stress test?
A cardiac exercise stress test shows how well your heart handles exercise. This can take various forms including stress ECG and stress echocardiograms.
The image below shows an exercise stress test.
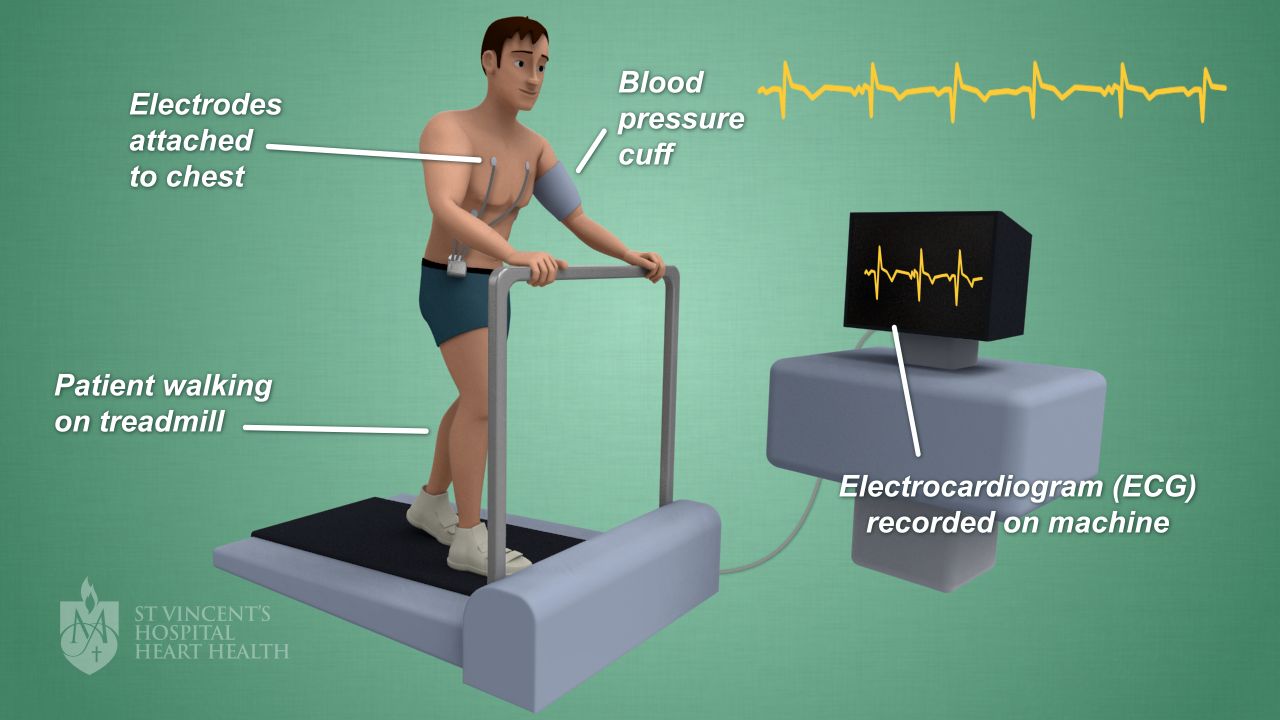
Why do I need a cardiac exercise stress test?
Your doctor may recommend a cardiac stress test to:
- Identify the cause of chest pain - as well as shortness of breath, dizziness and light-headedness
- Diagnose possible coronary artery disease - if you’re showing signs and symptoms
- Check the effectiveness of certain procedures - such as coronary angioplasty and stenting or cardiac bypass surgery
- Help create a safe exercise plan - if you have heart disease risk factors
- Identify any heart rhythm changes - usually experienced during exercise
- Determine your risk of heart disease - or other heart-related conditions
What are the risks of having a cardiac exercise stress test?
A cardiac exercise stress test is non-invasive and very safe. You’ll be accompanied by a nurse who will monitor your health and check for any concerns.
How do I prepare for an exercise stress test?
You can prepare for your cardiac exercise stress test by:
- Wearing loose, comfortable clothing
- Asking your doctor if you can take your medicine beforehand
- Avoiding eating - as well as smoking and drinking alcohol - at least 3 hours before the test begins
- Avoiding caffeine (such as tea, coffee, cola and chocolate) for 24 hours before the test begins
What happens during a cardiac exercise stress test?
During your cardiac exercise stress test, you’ll walk on a treadmill or cycle on an exercise bike until you reach your “target heart rate”- which is 85% of the maximum heart rate predicted for your age. Every 3 minutes, the speed, incline and resistance of your treadmill or bike will increase, up to 15 minutes maximum.
During the test, one or more medical professionals will monitor your ECG, heart rate, blood pressure and heart rhythm. They will stop the test if:
- You develop chest pain
- Your blood pressure is becoming a concern
- The ECG shows your heart isn’t getting enough oxygen
- You become too tired
- You have another symptom that prevents you from exercising
The test takes less than one hour in total.
What happens after a cardiac exercise stress test?
After you complete your cardiac exercise stress test, you’ll be monitored until your heart rate returns to its normal resting rate. Your test results will be explained to you, and your doctor may recommend additional tests and treatments.